

Alternatively, this probability can be directly read off a complementary cumulative Z table (described below). For example, to determine P(Z > z 1) subtract P(0 z 1). Therefore, P(Z 1.5), and can be found by subtracting P(Z z 1), by adding or subtracting the appropriate areas under the curve. Since 50% of values lie above and below the mean, the probability that a score will be below an 87 is represented by the following distribution: However, this probability only represents the probability from the mean to the Z-score, as shown in the figure below: Referencing the above Z table, a Z-score of 1.5 corresponds to a probability of 0.43319, or around 43%.
Use a cumulative from mean Z table to find the probability of a score being above or below an 87. The average score on a math exam for a class of 150 students was a 78/100 with a standard deviation of 6.
The x-value (and all values in the normal distribution) is standardized as follows: The figure below shows a normal distribution with μ = 5, σ = 4, and x = 11, as well as its corresponding Z distribution.
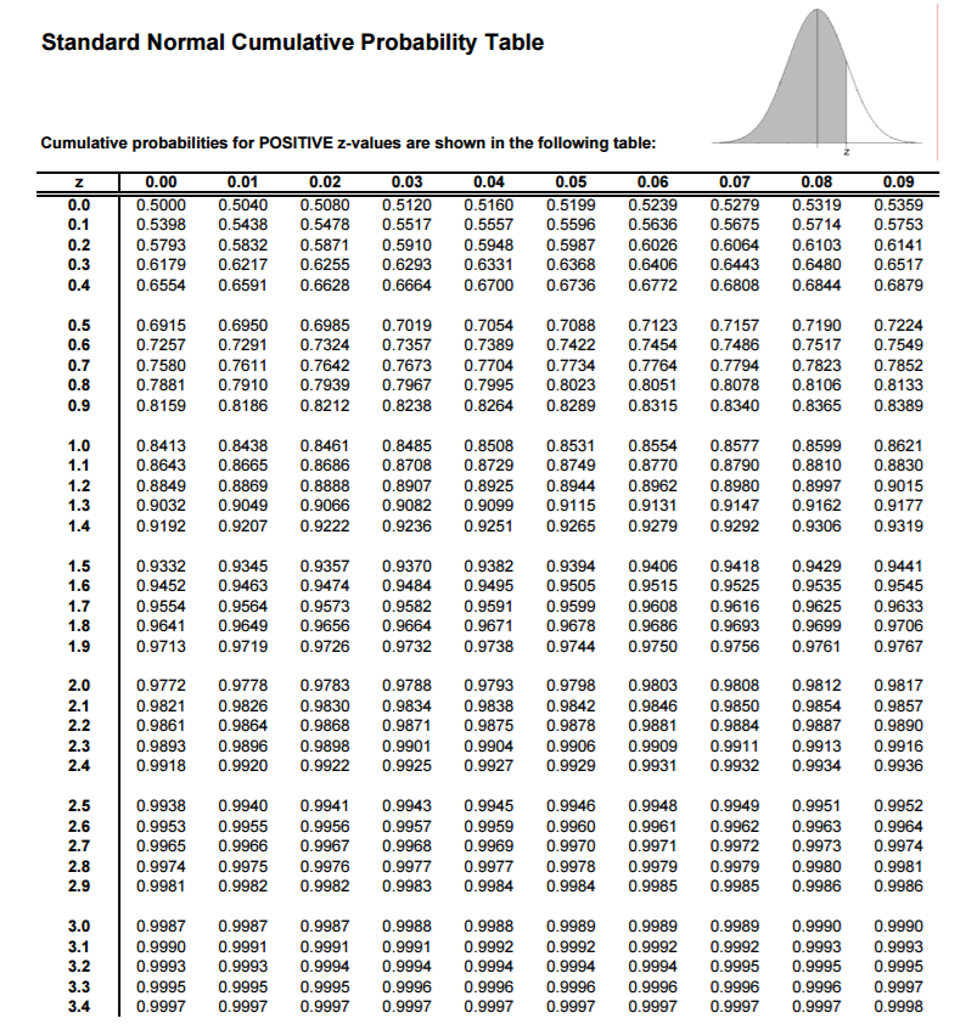
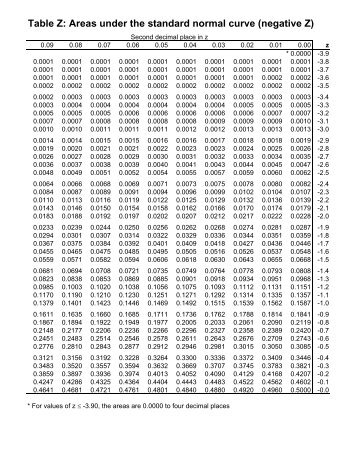
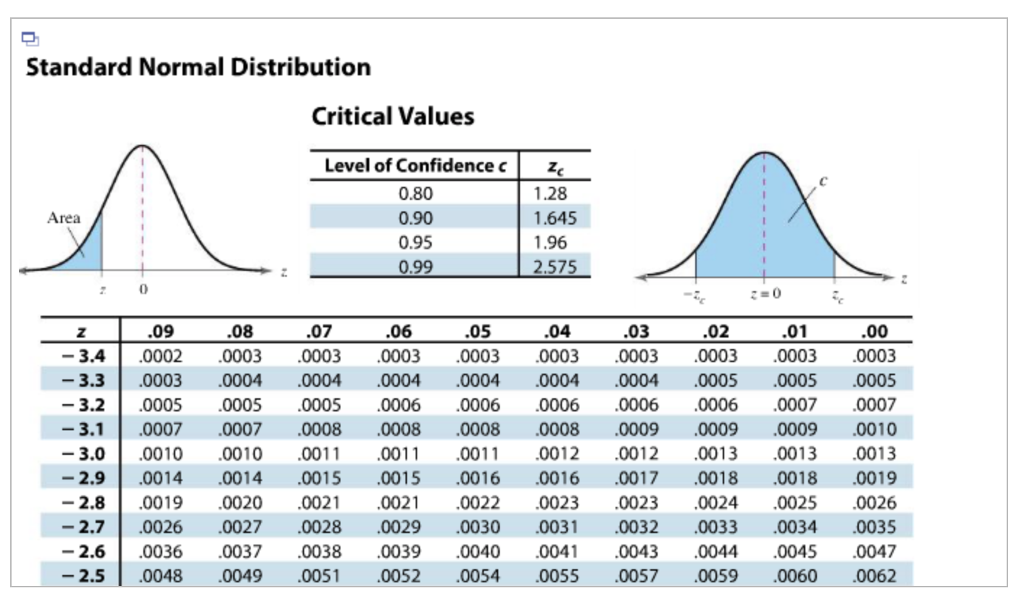
A Z-score of 0 indicates that a value is equal to the mean. A negative Z-score indicates that a value is below (left of) the mean. A positive Z-score indicates that a value is above (right of) the mean. A Z-score is used to determine where an observed value lies in a distribution, relative to its mean, and can be positive, negative, or 0: For example, a Z-score of 1 means that the value is 1 standard deviation from the mean. The resulting distribution of Z-scores is referred to as a Z distribution (or standard normal distribution), where the Z-score represents the number of standard deviations (not the value of the standard deviation) that a given value is from the mean. Where μ is the mean, σ is the standard deviation, and x is the value being converted. Z-scores and Z distributionsĪ normally distributed random variable can be standardized by converting its values to Z-scores using the following formula, However, since all normal distributions can be converted to a standard normal distribution, and since the associated probabilities have already been computed and compiled into Z tables for a standard normal distribution, it is possible to reference Z tables rather than having to integrate the pdf to determine the probability of outcomes within a given interval occurring. This is useful because, typically, it is necessary to integrate the probability density function (pdf) of a random variable to determine the probabilities of outcomes within an interval for the case of a normal distribution, this is particularly difficult. It tells us the probability that values in a normal distribution lie below, above, or between values on the standard normal distribution. Home / probability and statistics / hypothesis test / z table Z tableĪ Z table, also referred to as a standard normal table, is a table of the values of the cumulative distribution function of a normal distribution.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
